Gothic Architecture in the Middle Ages
 Gothic architecture originated in Western Europe in about 1100, and was popular in the building of cathedrals, universities, and many other structures until about 1500. At that point Renaissance critics called for a return to classic Greek and Roman architectural forms. However, during the mid to late Medieval years (in the Middle Ages), Gothic architecture flourished as an impressive art form.
Gothic architecture originated in Western Europe in about 1100, and was popular in the building of cathedrals, universities, and many other structures until about 1500. At that point Renaissance critics called for a return to classic Greek and Roman architectural forms. However, during the mid to late Medieval years (in the Middle Ages), Gothic architecture flourished as an impressive art form.
It is often, but not always, characterized by a structure of piers, flying buttresses, columns, elevated vaulted arched ceilings, intricate decorative features, round rose windows, narrow elongated lancet windows with pointed arches, ribbed columns and vaults and beautiful stained-glass windows.
Featured here: Amiens Cathedral Showing High Vaulted Arches, Rose Window in Distance (click here to see this larger)
The History of Gothic Architecture
The first Gothic building is thought to possibly be the Cathedral Basilica of Saint Denis, also known as the Abbey of Saint-Denis. This was built on an ancient historical site that started as a Gallo-Roman cemetery. In about 475 Saint Genevieve bought land there and built a church. In the 7th century that church was replaced by a much larger church building and some say the body of Saint Denis, the patron saint of France, was moved to the church at that time. This church became the burial site for French kings from about 900 through 1700.
Gothic: Architecture, Sculpture, PaintingCheck Price
In 1137 Abbot Suger decided to rebuild the church featuring a three-section fa̤ade and the first-known rose window. Other innovations in the building were pointed arches, a ribbed vault, clustered columns and flying buttresses. The Basilica was dedicated on June 11, 1144 Рperhaps the start of the Gothic architectural movement! This building still stands today, although what was originally a rural, communal area is now surrounded by a Parisian suburb.
Examples of Gothic Architecture
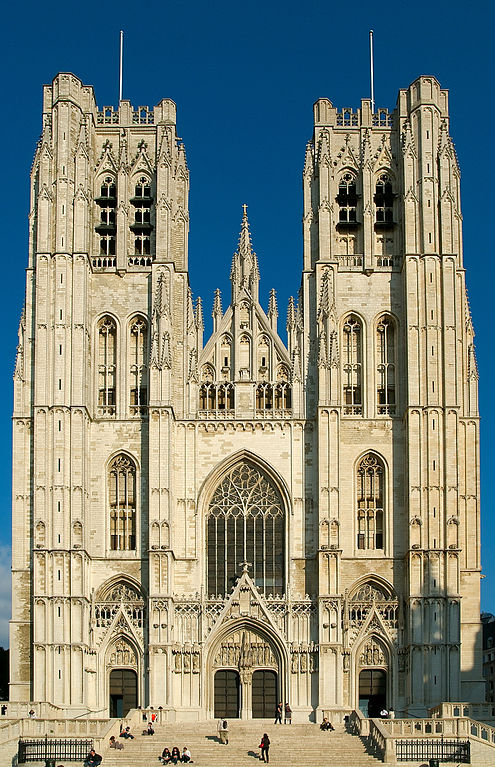
Source: I, Luc Viatour GFDL, CC-BY-SA-3.0, Wikimedia Commons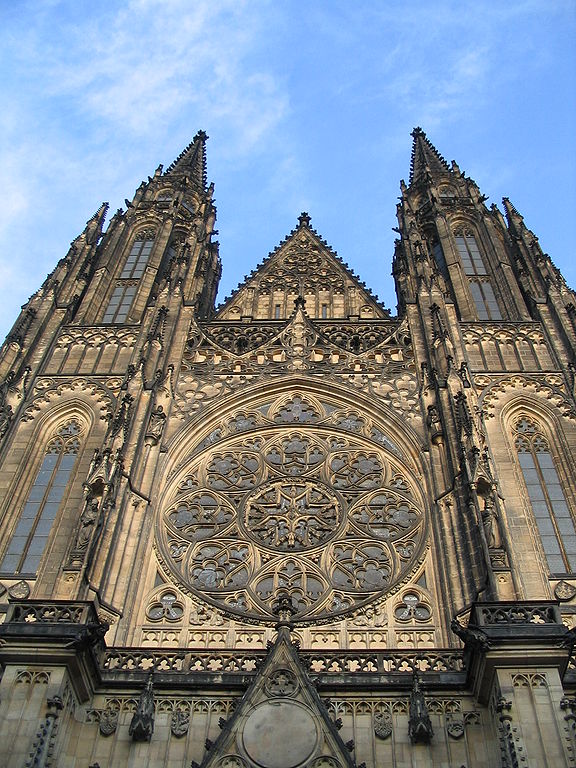
Source: Wikimedia Commons, CC 3.0, Valyag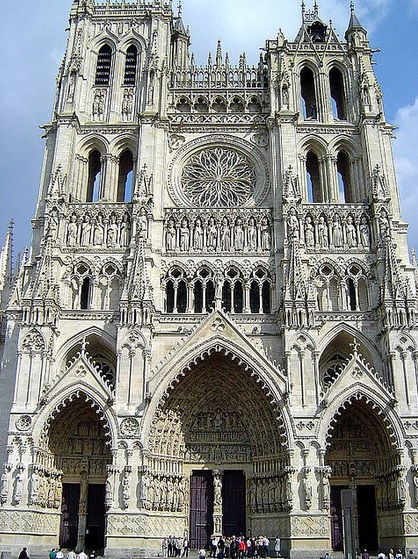
Notre Dame Cathedral Paris
Gothic Cathedrals
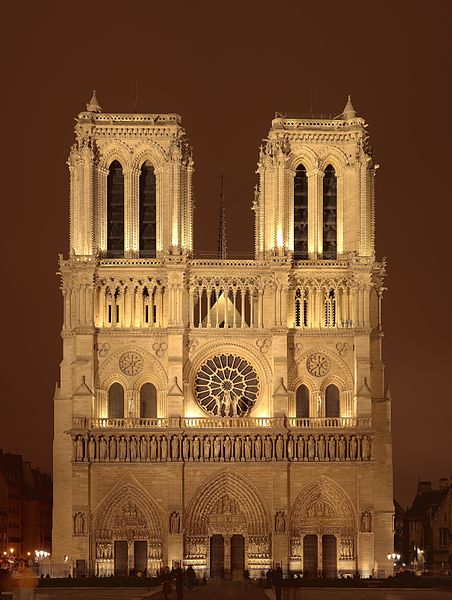

Source: By Sanchezn (Own work) GFDL or CC-BY-SA-3.0-2.5-2.0-1.0, Wikimedia Commons
One of the best known examples of classic Gothic architecture is Notre Dame in Paris, a cathedral constructed from 1163 until 1240, the exterior of which is decorated with frightening sculptures of grotesques, chimeras, and gargoyles. Gothic architecture is more than just a functional building; it is, in many ways, an impressive and unusual work of art. Other well-known examples of Gothic architecture are the Batalha Monastery in Portugal and the Florence Cathedral in Italy.
The Gothic Enterprise: A Guide to Understanding the Medieval CathedralCheck PriceThe Construction of Gothic Cathedrals: A Study of Medieval Vault ErectionCheck Price
The Goths
where Gothic came from
Gothic architecture was originally called Opus Francigenum, or “Frankish Work.” When the Renaissance started in the 14th century, Frankish Work fell out of favor. Those who wanted to revive classic Greek and Roman themed architecture chose to denegrate the older style of architecture, calling it “Gothic”.
This was a reference to the Goths, a warring and barbaric confederation of tribes from Germany and Scandinavia that invaded the Roman Empire starting with the sacking of Histria in 238. The Goths destroyed classical Roman and Greek art and architecture in the 400s. The Goths were associated with the art of making jewel-encrusted vessels, decorative objects and jewelry, but were not credited with the design of the famed architecture known as Gothic. Rennaisance writers including Christopher Wren and Georgio Vasari denegrated the Frankish Work architecture in their essays by referring to it as Gothic. Goths were considered vulgar, barbaric and rude, so use of the word “Gothic” was essentially an effort to brainwash people into hating it.
Times change and now Gothic architecture is admired, and few people remember that reference to Goths was an insult.
Bojeux Matchitecture – The Notre Dame de Paris CathedralCheck Price
York Minster Cathedral England – largest Gothic cathedral in Europe

Gothic architectural features were used primarily in churches and cathedrals, abbeys, synagogues, castles, palaces, guild halls, colleges, universities, and town halls, and sometimes in country houses and sometimes in private homes. But it is the churches and cathedrals we are most familiar with today.The Gothic style of architecture was intended to convey a spiritual message, especially when used in cathedrals. Elevated ceilings gave a sense of the loftiness and greatness of God. Geometrical elements spoke to the soul of an orderly, well-organized universe. Rich and intricate decorations on both the interior and exterior of Gothic cathedrals told Biblical stories and conveyed the history of saints for the edification of the faithful.
English Gothic cathedrals were known for their length, the French Gothic architecture, for ceiling height, and the German cathedrals, for their massive towers and spires as well as breadth.
Characteristics of Gothic Windows

Source: This photo was taken by Eusebius (Guillaume Piolle), Wikimedia Commons, Public Domain
This is the northern rose window of Chartres Cathedral. The rose depicts the Glorification of the Virgin Mary, surrounded by angels, twelve kings of Judah (David, Solomon, Abijam, Jehoshaphat, Uzziah, Ahaz, Manasseh, Hezechiah, Jehoiakim, Jehoram, Asa et Rehoboam) and the twelve lesser prophets (Hosea, Amos, Jonah, Nahum, Zephaniah, Zechariah, Malachi, Haggai, Habakkuk, Micah, Obadiah and Joel). Below, the arms of France and Castile
The five lancets represent Saint Anne, mother of the Virgin, surrounded by the Kings Melchizedek, David, Solomon and by Aaron, treading the sinner and idolatrous kings: Nebuchadnezzar, Saul, Jeroboam and Pharaoh.
These are typically Gothic in that window architecture featured tall narrow arched windows, described as elongated in proportion. The other Gothic window characteristics were display windows which were round or rose windows usually situated high a wall and meant to allow God’s light to illuminate those below.
Build a Model of a Gothic City Building
Pegasus Hobby Gothic City Building Small Set 2Check Price
Gothic Revival
Gothic architecture in the USA
A revival of Gothic architecture began in the 1700s in England. The Gothic revival architecture spread to Europe and other areas, well into the 1900s. It has been affectionately used for many recent universities and churches. Gothic revival architecture of the 19th and 20th centuries can be seen in many parts of the world including England, France, Germany, Austalia, New Zealand, Thailand, Japan, Mexico, the USA, and Canada. Examples are Westminster Palace in London, and the Cathedral of Saint John the Divine, St Patrick’s Church and Trinity Church in New York City.
Gothic Architecture (The Yale University Press Pelican History of Art)Check PriceThe Gothic CathedralCheck PriceThe Formation of English Gothic: Architecture and Identity, 1150-1250 (The Paul Mellon Centre for Studies in British Art)Check Price